Scalability
CS-A1120 Programming 2
Lukas Ahrenberg
Department of Computer Science
Aalto University
(Based on material by Petteri Kaski and Tommi Junttila)
After this round, you
- are aware of how computing can be scaled up and distributed
- are familiar with Apache SPARK's Resilient Distributed Dataset
- can write a program that uses Apache SPARK do distribute computing
This week's exercises: make sure you use JDK 11!
Apache SPARK is picky, and will throw exceptions.
- VS Code (follow instructions in notes)
- Install JDK 11
- Set java home in Metals settings if needed
- IntelliJ
- File → Project Structure → Project & choose/add SDK
What if one computer is not enough?

- Common crawl
- Public web crawl data
- January 2022 crawl set (source)
- 2.95 billion web pages
- Data size: 320 TiB
- Access via Amazon Open Data registry
How can data like this be processed?
Background: AWS Snowmobile data truck. Capacity 100 PB
Warehouses, Clusters, Grids …
Scalable distributed computing infrastructure
Warehouse-scale computers
- E.g. for hosting internet services (search engines, video streaming, …)
- Extremely homogeneous and hierarchical
- One building with cooling and electricity
- Specialised hardware & software
- Operated by big companies
- Services are virtualized
Compute clusters
- Networked set of computers (nodes)
- Homogeneous
- Nodes are physically close (same rack/hall)
- Each node work on the same task
Computing grids
- Networked set of computers (nodes)
- Heterogeneous
- Geographically dispersed
- Nodes usually work on different tasks
How can warehouses full of servers be programmed?
In general
- Network of computers
- Can be viewed as a single computer
- Each computer is a node in the network
- Physical constraints
- Bandwidth
- Latency
- Data set needs to be distributed
- Limited RAM and storage in each node
- Nodes fail
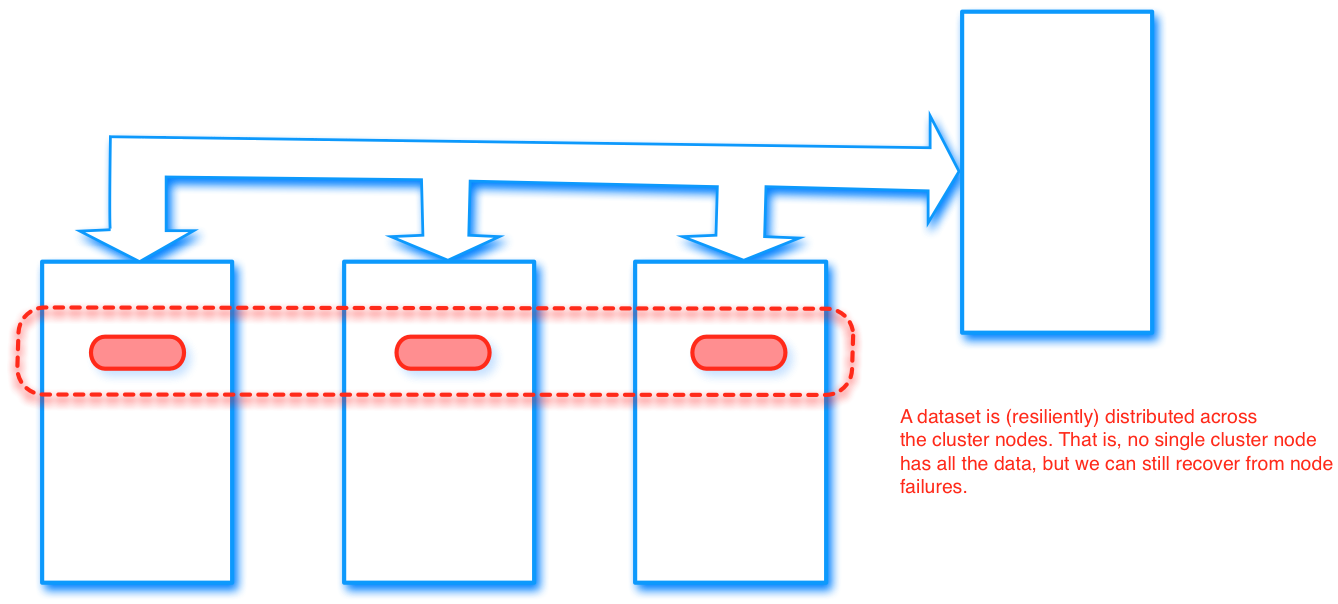
- Data is partitioned over nodes, and
- maintained so that it is resilient (fault-tolerant)
- Workflow is scheduled to enable recovery (by re-computation) in case of failure
- Efficiency is dependent on
- partitioning
- persistence (caching)
- dependencies
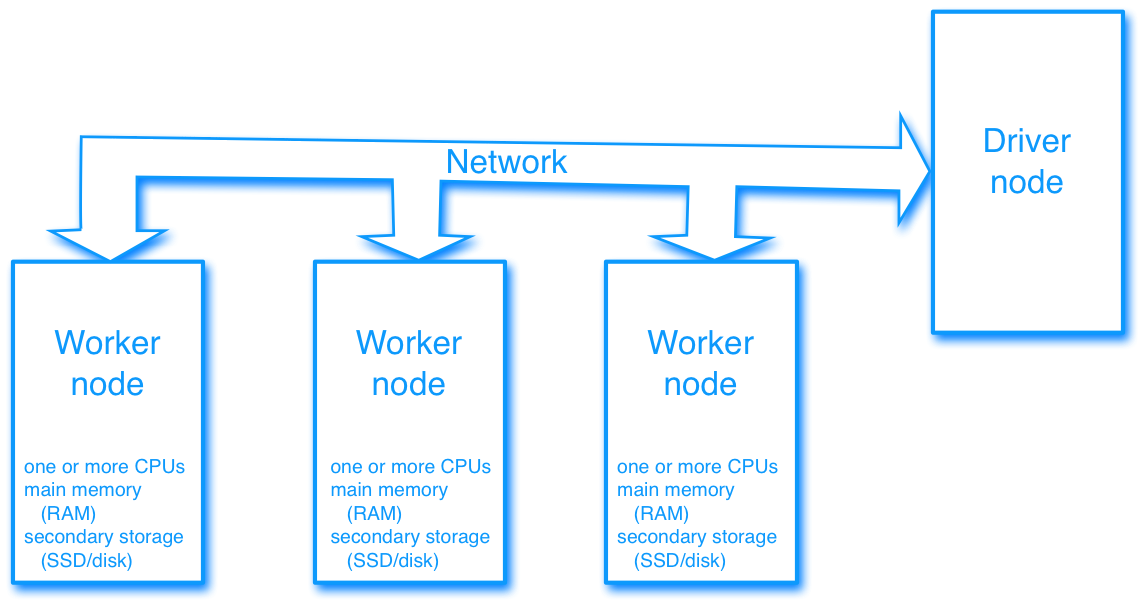
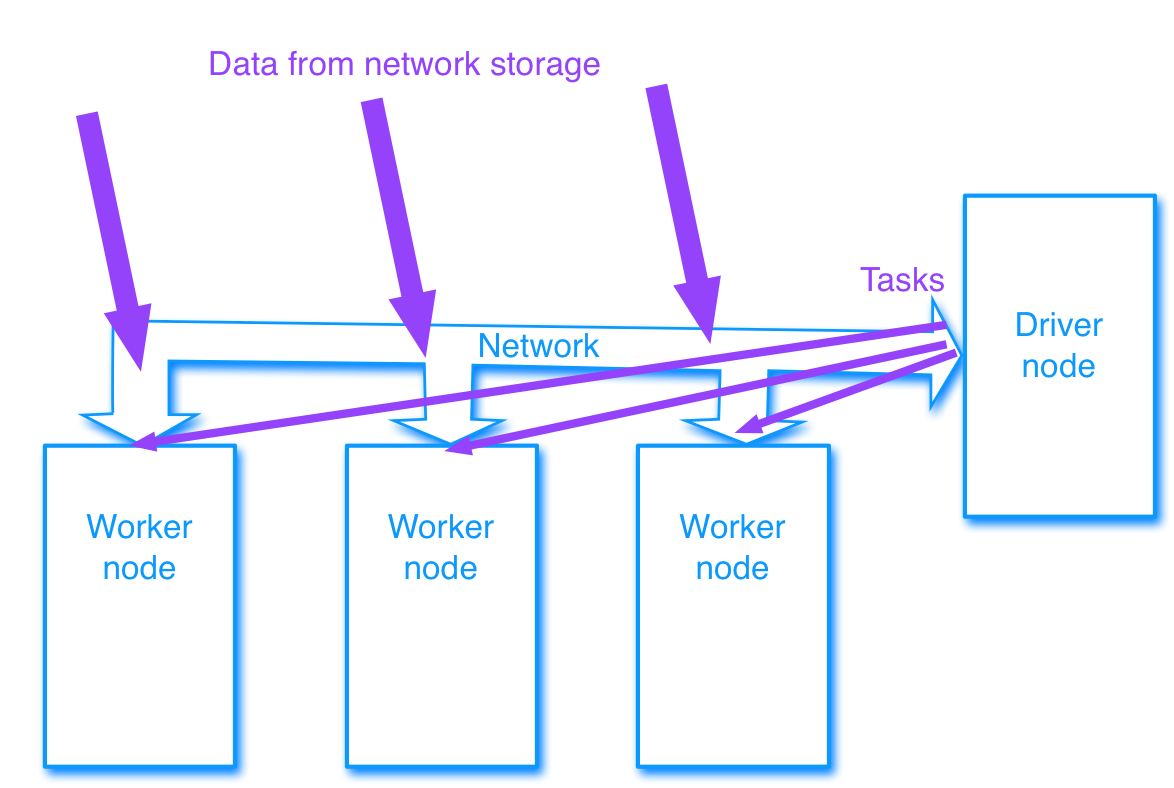
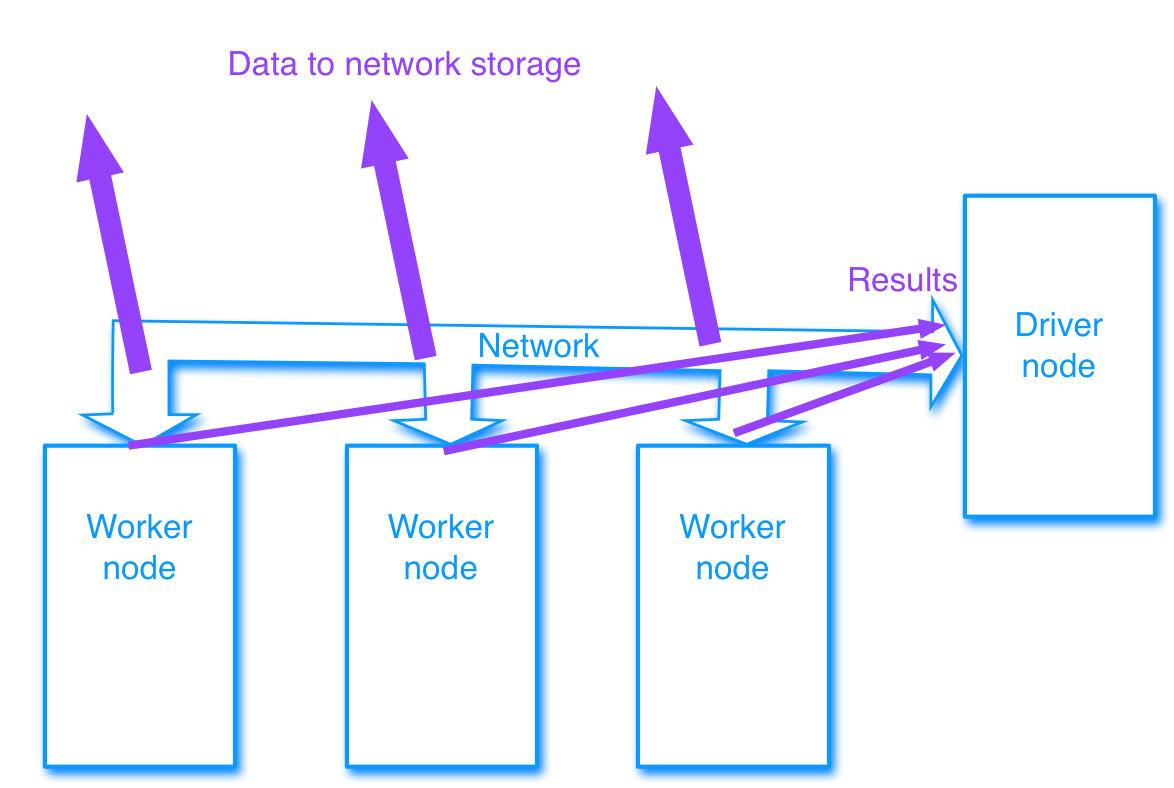
Driver node and worker nodes
- Designate one node as the driver
- Controls the operations of the workers
Driver node and worker nodes
Driver node and worker nodes
Easily distributed computing
- Apache Spark
- Driver program
- Executes parallel operations on a cluster
- Two main abstractions
- Resilient Distributed Datasets (RDD)
- Dataset
- Dataset is a newer abstraction and based on Spark SQL.
- We will focus on the basic RDD

- Bindings for Scala, Python, Java…
Resilient Distributed Datasets - RDD
Apache Spark RDD Programming Guide
Resilient Distributed Datasets - RDD
- A fault-tolerant collection of elements
- Can be operated on in parallel
- From a high level: similar to a Scala collection
- Transformations
- Create a new dataset from an existing one
- E.g.
map
- Actions
- Run a computation and return a value to the driver program
- E.g.
reduce
RDD transformations
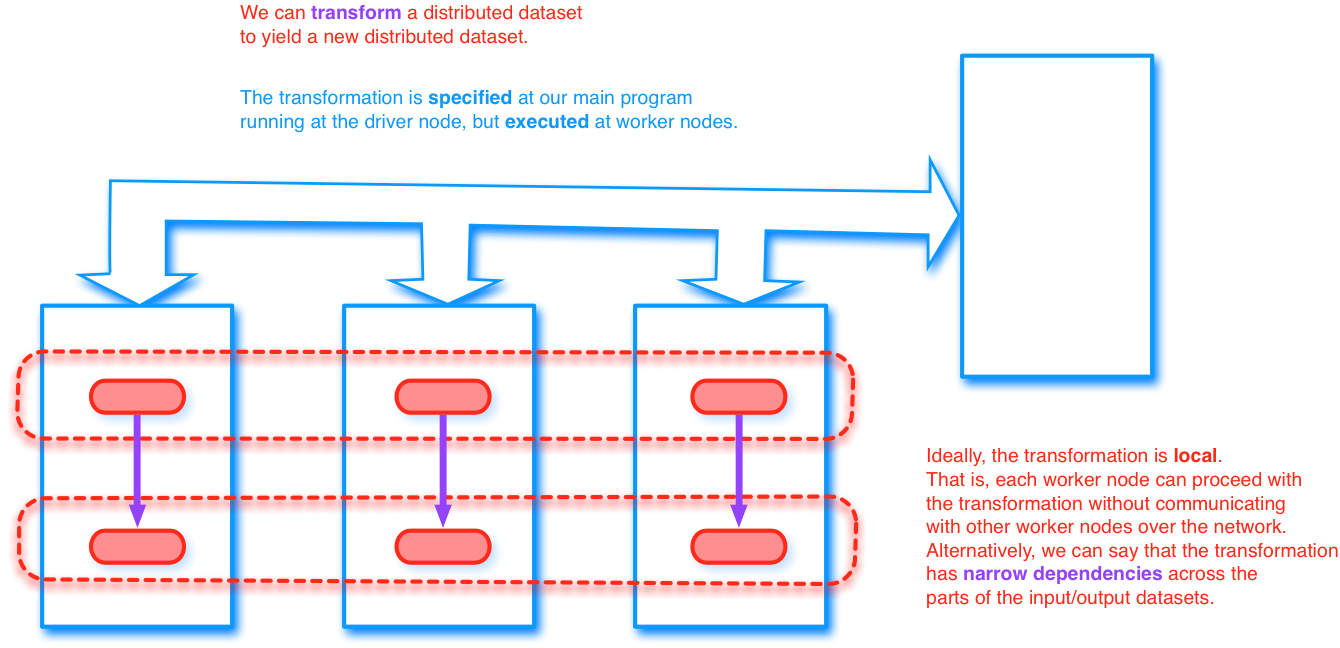
RDD transformations
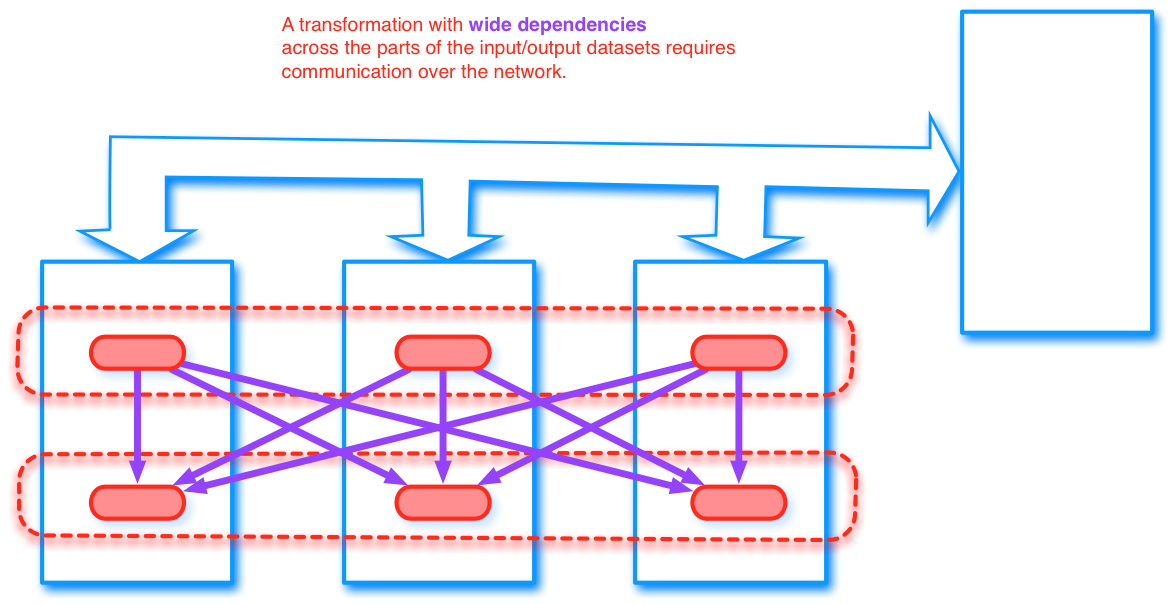
RDD transformations
Examples:
map(func) |
Return a new distributed dataset formed by passing each element of the source through a function func. |
filter(func) |
Return a new dataset formed by selecting those elements of the source on which func returns true. |
union(otherDataset) |
Return a new dataset that contains the union of the elements in the source dataset and the argument. |
intersection(otherDataset) |
Return a new RDD that contains the intersection of elements in the source dataset and the argument. |
distinct([numPartitions])) |
Return a new dataset that contains the distinct elements of the source dataset. |
groupByKey([numPartitions]) |
When called on a dataset of (K, V) pairs, returns a dataset of (K, Iterable<V>) pairs. |
sortByKey([ascending], [numPartitions]) |
When called on a dataset of (K, V) pairs where K implements Ordered, returns a dataset of (K, V) pairs sorted by keys in ascending or descending order, as specified in the boolean ascending argument. |
Full list available here
- Functions should be pure
- Closures might not work as expected
- Transformations are specified on the driver and distributed to the workers
RDD Actions
Examples:
reduce(func) |
Aggregate the elements of the dataset using a function func (which takes two arguments and returns one). The function should be commutative and associative so that it can be computed correctly in parallel. |
collect() |
Return all the elements of the dataset as an array at the driver program. This is usually useful after a filter or other operation that returns a sufficiently small subset of the data. |
count() |
Return the number of elements in the dataset. |
take(n) |
Return an array with the first n elements of the dataset. |
Full list available here

Writing a Spark program in Scala
Create a
SparkContext, e.g// Connect to `cluster` and call app `name` val sc = new SparkContext(cluster, name)Set up RDD, e.g
// Create RDD from local collection `inputs` val parInputs: RDD[Int] = sc .parallelize(inputs)- (Data can also be read from local or distributed file systems)
Apply transformations, e.g
// Map function f over RDD val parTransf: RDD[Int] = parInputs .map(input => f(input))Apply actions, e.g
// Reduce by multiplication of elements // result to local variable `total` val total = parTransf.reduce(_*_)- Repeat as needed
Example Spark program
- Let's say that we have a (large) set of data logging multiple test scores for participants in a test.
- Multiple values are logged for each paticipant.
.
.
.
7ANX6 : 26
7ANX6 : 55
KY76X : 23
DZJQR : 31
SSRU2 : 90
KY76X : 12
SSRU2 : 87
.
.
.
- What is the sum of data values for each paticipant, after discarding outliers?
- Let's use spark:
- Create a
SparkContext - Set up RDD
- Apply transformations
- Apply actions
- Create a
Example Spark program
import org.apache.spark.SparkContext
import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD
@main def main() =
// Set up context
val sc = new SparkContext("local[4]", "example")
// File of data pairs, e.g. id and points
val rawData : RDD[String] = sc.textFile("data.txt")
// Split at ',' and convert second column to double
// Note ASSUMES well formatted file
val data : RDD[(String, Int)] = rawData.map(x =>{
val cols = x.split(":")
(cols(0).trim(), cols(1).trim.toInt)
})
// Filter on values in a certain range,
// e.g. to get rid of outliers
val filtedData : RDD[(String,Int)] =
data.filter((_,v) => (v > 5 && v < 95))
// Calculate sum of values for each key value,
// then get results
val keySums : Array[(String, Int)] =
filtedData
.reduceByKey(_+_)
.collect()
// keySums contains the data collected,
Exercises
- Word statistics
- Transaction statistics
- Challenge: PageRank
- A bit different exercise submission
- Update / run
*Run.scalafile - Copy relevant
OUTPUTto*Solutions.scalafile - Submit both files
- Update / run
- Spark can output a LOT of text.
- The Filter box in VS Code can prove useful.
- First exercise is really easy
- Just run it and copy the output
- Exercises this round has no unit tests, it is up to you to test the programs
- Expected output can in many cases be found in the source code, make sure to read it
- Consult the Spark Documentation (Guide, API)